Sportsman Hernia
Definition
A Sportsman Hernia is not true hernia and it is also know as a Sports hernia, Sportsmans’ hernia, Gilmore’s Groin, Athletic Pubalgia, Inguinal Disruption or Groin Disruption.
This condition was first described in 1980 but it is still not very well understood and known between clinicians.
A Sportsman hernia mainly affects men, high-performance athletes or professionals who perform high agility/intensity sports (that involve frequent twisting, turning) such as football, rugby, athletics, hockey, etc.

Clinical presentation
The typical features of a Sportsman Hernia is a constant dull, sharp or burning pain around groin or lower abdomen which radiates to the testicle, lower back, pubic bone or upper thigh. The pain gets worse after exercise, lifting or increased physical activities and resolves with rest but usually appears immediately after return to sport.
On clinical examination there is usually no visible or palpable lump in the groin but sometimes weakening of groin wall, but on palpation or extensive pressure the groin is painful. Also extensive hip movements can trigger groin pain.
Cause
Pain in a Sportsman Hernia comes from injured muscles and tendons in the groin near the attachments of abdominal muscles to the pubis, due to abnormal tension in the groin during extensive physical activity; in combination with the weakening of the muscles and tendons in lower abdominal wall.
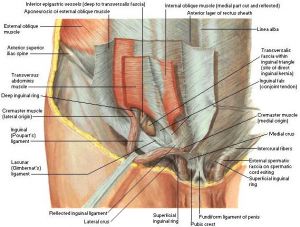
Main features of groin disruption include
- Tear on external oblique muscle
- Tear on conjoined tendo
- Disruption between conjoined tend and inguinal ligament
- Disruption of conjoined tend from pubic tubercle
Unlike a traditional hernia, the sports hernia does not create a hole in abdominal wall.
Diagnostic
Medical history in combination with clinical examination is crucial in diagnosis of a Sportsman Hernia. Generally, examination does not reveal an actual hernia.
Typical symptoms
- Dilated deep inguinal ring and presence of cough impulses.
- Tenderness at pubis region.
- Adductor weakness.
In cases when a diagnosis is unclear additional radiological investigation might be required.
Radiological Investigation
Ultrasound and MRI scan are preffered investigation methods to diagnosed Spostsman Hernia. Usually these scans identify weakness of the groin wall and groin tissue oedema (injuries on the muscles and tendo). However there is no any specific feature typical for Sportsman Hernia. In addition, these imagings are applied to rule out other groin pathology.
Differential Diagnosis
- Groin Hernia
- Femoral hernia
- Tendopathy
- Neuropathy
- Bursopathy
- Osteitis Pubis
- Necrosis of femoral head
Treatment
For the best results, management of a Sportsman hernia requires a multi-disciplinary approach. This includes medical treatment, tailored physiotherapy and surgical intervention.
Medical treatment
This treatment is initially applied to control pain when the patient presents with the problem. It includes anti-inflammatory analgesics and in some cases injections of corticosteroids, combined with prolonged physical rest.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is a crucial part of the management of a Sportsman Hernia. Rehabilitation involves core stabilisation exercises and the maintenance of muscle control and strength in pelvis. A specific functional rehab program is designed to target individual needs for best results.
Surgery
The surgical technique of Sportsman Hernia comes from a standard hernia repair. Surgery involves groin reconstruction, releasing abnormal tension in the groin canal (concurrent adductor tendon) and groin reinforcement with a mesh or sutures.
Nowadays, laparoscopic approach has shown excellent results with high success rates to control pain, low morbidity and faster recovery.
Generally, surgical intervention is more effective than conservative treatment in the management of groin pain!
To achieve the best possible outcomes for the management of a Sportsman hernia it must be multi-professional, including physiotherapy and surgery. Every patient is carefully assessed and treatment is tailored according to clinical conditions and patient needs.
In my practice I closely cooperate with a chiropractic (Mr Rainer Wieser; Doctor of Chiropractice) who is highly specialised in sports injury and Sportsman hernia.

