Gallstones diagnosis
Most of the stones are asymptomatic and found incidentally when a patient is having investigations for other reasons. However, you should see your doctor If you experience some of the gallstone symptoms.
First of all a doctor takes your medical history and examines you, requests blood tests and ultrasound. Blood tests are requested to check for stone complications (biliary obstruction, inflammation, etc). An Ultrasound is used to identify stones. It is quick and painless test. On some occasions, when diagnoses are unclear or you developed complications, doctors may request additional tests i.e. MRCP (Magnetic resonance cholangio-pancreatography), CT (Computer tomography), HIDA scan (Cholecystography), ERCP (Endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography) or EUS (Endoscopic ultrasound).
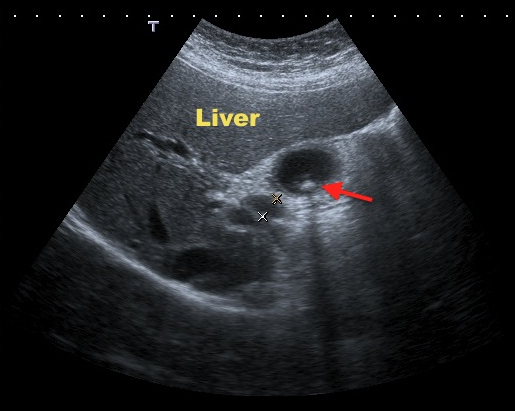
Ultrasound of the gallbledder: Red arrow is pointing on gallstones in the gallbladder.
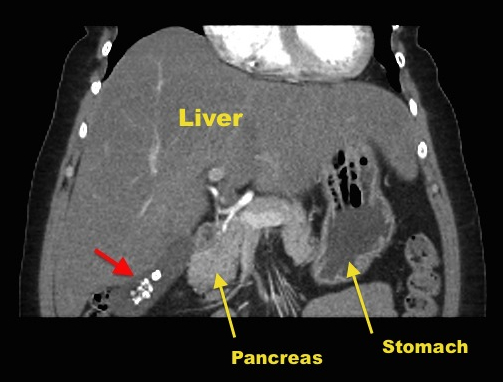
CT Abdomen: Red arrow is pointing on gallstones in the gallbladder.
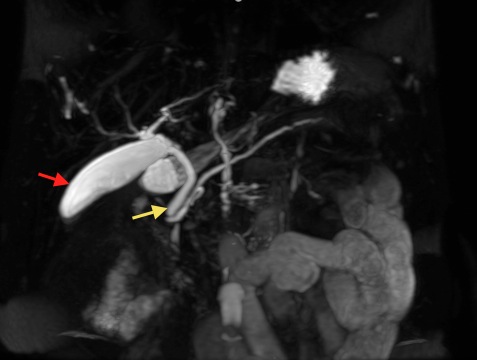
MRCP: Red arrow is pointing on the gallbladder. Yellow arrow is pointing on the common bile duct.
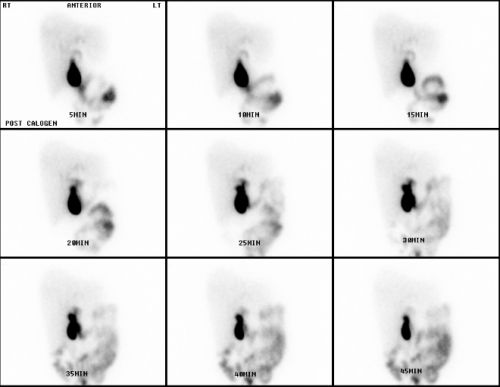
HIDA scan (Cholescintography): The scan uses radioactive chemicals to track bile flow from liver to small inerstine and also evaluate gallbladder.